


TECHNICAL OPERATING RULES
CHAPTER ONE
BASE TERMINOLOGY
| Basic Terms |
|
> OPERATOR: A person trained to operate in the stands in full or in a sector. > END SEASON: The season that is where the tour ends. > SIGNAL CABIN: building usually in a tower from which control signals and changes via a Apeadero or station, may be coordinator with the CTC system. > Apeadero: A school that opens via the main able to rejoin or not, by and large they are way stations or farms, industrial, mining or commercial. > BRANCH: Derivation of Way from the main line to another area or location. > LOCOMOTIVE HOLDER: The marching at the head of a train, or the tail if PUSH AND PULL formations. > LOCOMOTIVE AUXILIARY: The train that helps. > LOCOMOTIVE LIGHT OR SINGLE: The train runs smoothly and without any drag. > LOCOMOTIVE PILOTS: The maneuvers designed to service. > TANDEM: A set of 2 to 6 locomotives that can travel together alone or head of a train. > CARS: The leading passenger rail vehicles. > CARS: The carrying loads. > OBSTRUCTION: any vehicle is stopped, via damaged, and in general anything that jeopardizes the progress of trains. > TRAIN OR TRAINING: For the purposes of the service, train or training is considered, to all vehicles traveling on sections of a lining. > Or FAST EXPRESS TRAIN: Train passengers or cargo that has right of way within the line. > NEAR OR LOCAL TRAIN: Train passengers and / or charges flowing short distances between stations, or branches. > HELP TRAIN: Training for emergencies or accidents, usually consisting of a crane, two cars and a car support workers. > TRAIN FACILITIES: Train dedicated the branch's own internal traffic such as coal trains, roads and works, etc.. > CTC Centralized Traffic Control, a position that controls and organizes the traffic in the lying. > CANTON: Sector of a CTC can be controlled by remote means or the signal of the cabin. > DEVICE VIA: any change is made up of crosses or hearts, hands and rails. > CHANGE TIP: It's all change for the train to take first the end of their needles. > CHANGE OF HEEL: the train is taken primarily from the end of your heart or cross. > WAYS OF RUNNING: There are main roads and general and auxiliary used for movement, passing and passing trains. > WAYS TO TIP: those affected by parking. (Tiraderas, maneuvering tail, leakage, or domestic service). > DEVIATION: roads are designed to perform maneuvers or diversion of vehicles to roads and pathways > VIA UP: Is that why the train follows the direction of lower to higher mileage. > VIA DOWN: Is that why the trains are in the direction of higher to lower mileage. > TURNTABLE: The platform, a way that allows investment in locomotives and vehicles. > TRIANGLE: The mechanical system that moves through March 3 (2 forward and 1 reverse) allows deviations through 3, the practice of investment vehicles. > LOOP: Is one branch, that through a curve, pronounced splicing itself, investment and allows trains or vehicles individually. |
Article 1: The trains will arm or disarm only terminal stations, beaches and inland 3ras., Empowered to do so.
Article 2: The training must travel with signs of tail. They will only do they have the same, being the authorized: the rangefinder, red lights, or caboose caboose, cabin decelerate, signal discs, red flags, or a car or passenger van. Since this article exeptuante in light locomotives. Article 3: No trains may move inconsistent with hooks attached to each other to avoid cutting of formations. Article 4: It takes into account the following points for the proper functioning of lying:|
A) Clean wheels. B) Cleaning of roads. C) The correct polarity of vículo engine (locomotive). D) The proper level of hooks. E) The free bearing axis. F) The distance between stops or bellows. G) The proper gauge of the model. |
Article 5: It is advisable not to transport any loose cargo.
Article 6: It is advisable, in the assembly of trains, cars or placing heavy wagons following the motor vehicle, and the lightest at the end. Article 7: the movement of trains in case of parallel tracks will be on the left (English system) or right (USA system) Article 8: the trains will be coded according to actual existing rail standards as follows, according to their priority:|
01) Train assistance, relief, auxiliary engine; 02) Train internal super express service:, 03) express passenger train and / or collector; 04) local passenger train; 05) Train closed; 06) Train perishable goods - Express; 07) Train perishable goods; 08) Train general charges (rocks, dust, packed, etc.). 09) Train loads empty 010) Train local charges; 011) Locomotive light holder; 012) Locomotive pilot; 013) Zorras inspection. |
Article 9: Veículos disengagement may be effected release clamps or plates (type or KADE NEM). If no such elements may be made by hand.
Article 10: The trains will run at moderate speed, especially at the passing point changes, zone changes and coupler modules. Article 11: It must be observed in all cases, caution boards permanent or temporary, in which is indicated the speed at which trains must travel. Article 12: In maneuvers, should be observed especially at moderate speed back and dock, be used as a guide the following table of rates:
| TRAIN TYPE. | VELOCIDAD EN SCALE (sec / met.) |
VELOCIDAD REAL (km./h) |
| EXPRESS PASSENGER TRAIN. | 2 | 150 |
| LOCAL PASSENGER TRAIN. | 3 | 100 |
| TRAINS LOCAL CARRIER and CARRIER. | 6 | 50 |
| TRAIN OPERATIONS OR AREAS OF CAUTION. | 12 | 25 |
| LOCOMOTIVES TO TAKE SERVICE: PILOTAS OCCASIONAL HOLDERS. |
12 3 3 |
25 120 120 |
Article 13: The control of vehicles by cantons or between stations will be controlled individually or jointly by each operator, through the card system or spreadsheet. Not be able to use both systems simultaneously, as they are not compatible. It is up to the traffic control system used in each operation as well as the instruction to use due operators thereof.
CHAPTER THREE
GENERAL RULES
A BOARD INDICATORS
Article 14: Dashboard speedometer fixed.
Used to indicate the maximum speed level, expressed in km / h, which trains must travel
a given stretch of road, are diamond-shaped, usually white with black markings.
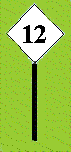
B) At the point where a board begins caution as above, but carrying an extra sign at the bottom, indicating the observed speed in km / h. If the same stretch of road but later, would need to establish a different speed, placing an equal board with the corresponding speed. This will also be white with black numbers.
C) The end point where the restriction is placed like a checkerboard design as above but with a letter T in the extra poster, or a green sign with white edges without numbers or letters, they are both perfectly valid.
Article 16: Indicator panels limit maneuvers, beginning or ending of signaling system, rail or tip. In all cases will be white with standard font in black:
A) is used to indicate the extent to which they can move the trains to carry out maneuvers.
B) indicate the beginning of a certain type of sign, or speed to take throat of changes to certain sectors. (Beaches, sheds, side branches, etc.).
C) indicate the end point of roads or rails. Were placed at 300 meters., 200 mts., 100 mts. before the caution.
Article 17: Stakes indicator gauge crossing or pickets.
Are used to indicate the ends of the crosses in track switches or changes.
Identified to bring the left half white and red on a board right triangle with
point upward, located on a pole.
Article 18: Stakes decoupling indicator plates.
Indicate the area of road on which they are located or release decoupling plates.
Identified to bring the left and right orange yellow
a triangular board with the top down. Are placed next to the system.
They are located on the floor in a small post.
Article 19: Stakes indicator for the speed control.
Listed in a section of each circuit of a meter distance corresponding real
is used to control the speed of trains according to Article 47 of Chapter III,
to verify the passage of a train between two signals of these with a second clock.
Be identified as being a completely white triangular board, with the top down.
Article 20: Records of approach.
Were placed at 100 meters in scale will be announced before the white background
black type.
A) indicates approaching season.
B) Indicates approach to stop or halt.
C) Indicates approach to bridge.
Article 21: Indicator panels whistle.
Not be mandatory, as there are no currently too many models with speaker systems functional. But may be placed to improve the scenery or exemplify the real driving instruction trains.
Be rhomboidal, with white background and black typeface (letter S).
It also placed 100 mts. scale, before a pedestrian crossing, level crossing or any other special reason.
CHAPTER FOUR
GENERAL RULES GOVERNING SIGNS
Article 22: We recommend the use of traffic signals, mobile or light, for best performance and agile movement of trains. This provision is not mandatory, about their placement.
Article 23: Shall be liable to sanction anyone main road operator or internal, that violates a signal at danger on purpose, being able to move east with their training to the foot of the signal inclusive.
Article 24: The drive systems and their location and design shall be free from its owner who will take into account primarily the effectiveness of the design and use.
Once in operation, submit to the Technical Commission of the module design, location of traffic signs, panels, indicators etc. so that it instructs the other operators on the practice track.
Article 25: Here are the two types of traffic signals exist: mechanical or boards and bright.
With regard to mechanical signals must be interpreted from his red face, white face being opposite and not operable.
| MECHANICAL | LIGHT |
| A)
|
|
| B)
|
|
| C)
|
|
| D)
|
Risk Free Way |
| E)
|
|
| F)
|
|
|
Signs that route (valid for such mechanical and / or light) the same may be fixed. Indicates whether or not to move to that section of road, walk, etc. |
|
| G)
Arms seen from behind |
Semaphore seen from behind |
| H)
|
|
1) Two aspects, 2) Three aspects
B) arm signals caution:

2 aspects signals do not have this option. If the three aspects, that is the one that follows
C) signs a free-arm:
2 types of ways, listed 45 degrees, and three areas to 90 degrees.
Article 27: Location of signs on poles, frames or poles (Valid for both systems.)
In general, the poles that carry the mobile signals are installed on the left side of the road rule, depending on the direction of the train, unless for reasons of visibility or space should be located elsewhere.
A) When a pole or mast that has two or more arms or lights at different heights, the highest governing the main road and the height of the other corresponds to the importance of their respective tracks.
Example:
B) When the arms are placed at the same height, on the same mast or gantry, the left signal will govern the way left and right to the right track. This indicates that it is 2-way with equal importance.
Example:
C) While the location of masts different signal or signals are at a lower level indicates the position of the track or tracks in relation to the most important.
Example:
D) The location of signs will be minor as he said, lower than those of major importance. except where otherwise indicated crossing route.
Example: